
Ethereum smart contracts are being used to hide malicious URLs, making them harder to detect.
The malware packages (colortoolsv2 and mimelib2) were hosted on NPM and appeared legitimate.
Blockchain traffic is trusted, so security systems often overlook it.
Fake GitHub repositories were used in a coordinated social engineering campaign.
This trend marks a shift in malware tactics targeting Web3 infrastructure and open-source software.
ReversingLabs researchers revealed that two NPM packages, colortoolsv2 and mimelib2, published in July 2024, were designed to use Ethereum smart contracts to hide and retrieve URLs associated with malware payloads.
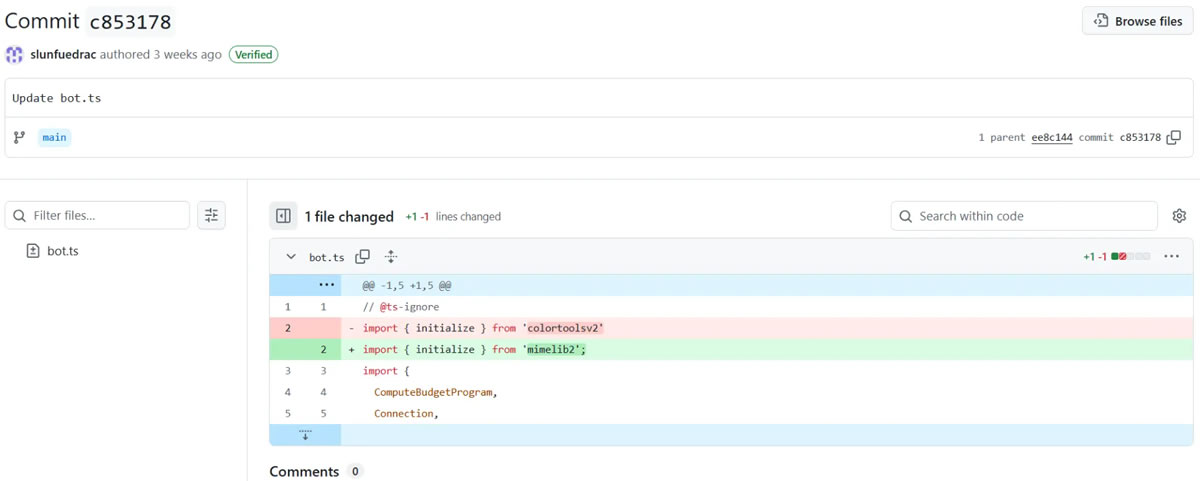
NPM packages ‘colortoolsv2’ & ‘mimelib2’ On GitHub
Source: ReversingLabs
Instead of embedding malicious URLs directly into the packages, the malware fetched command-and-control (C2) server addresses from Ethereum smart contracts, making detection by conventional security tools significantly more difficult.
Because interactions with the Ethereum blockchain are considered legitimate network traffic, querying smart contracts to obtain malware download URLs can go unnoticed by traditional intrusion detection systems.
Once installed, the malicious packages acted as lightweight downloaders, initiating communication with the blockchain to retrieve hidden instructions.
ReversingLabs researcher Lucija Valentić said:
“What is new and different is the use of Ethereum smart contracts to host the URLs where malicious commands are located.”
These malware packages weren’t isolated threats, they were part of a larger deception campaign. Hackers set up fake GitHub repositories that mimicked legitimate cryptocurrency trading bots.
Tactics used to build trust included:
Fabricated code commits
Fake user accounts to simulate popularity
Multiple maintainer profiles
Professional-looking documentation
These repositories lured developers into downloading and integrating malicious packages into their projects, unknowingly exposing themselves to malware.
This attack strategy reveals a troubling trend: open-source repositories are becoming attack surfaces.
As developers increasingly rely on packages from NPM, GitHub, and other open repositories, threat actors are embedding themselves in the supply chain.
Ethereum smart contract malware isn’t entirely new. The infamous Lazarus Group, believed to be linked to North Korea, used similar techniques earlier in 2024.
However, this latest approach introduces a new level of stealth and complexity.
Other blockchain ecosystems have also been targeted:
Solana: A fake GitHub repository posed as a Solana trading bot and delivered obfuscated malware to steal wallet credentials.
Bitcoinlib: A legitimate Python library used by Bitcoin developers was exploited to inject credential-stealing code.
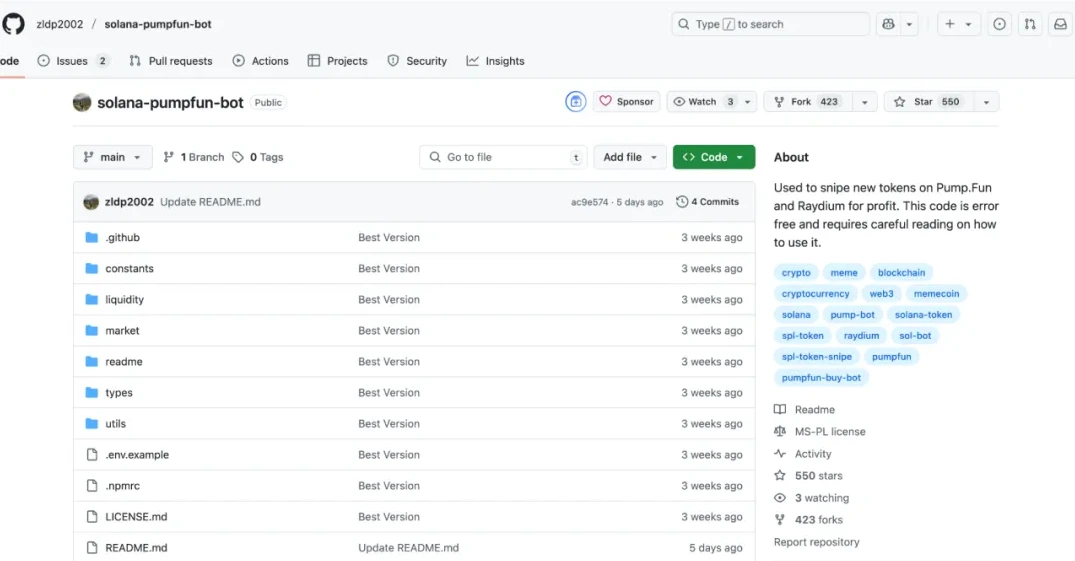
The Now Deleted Fake GitHub Repository
Source: SlowMist
In 2024 alone, researchers have documented over 23 malicious campaigns targeting crypto-related open-source repositories. This new use of Ethereum smart contract malware shows that attackers are continuously refining their tactics.
Traditional malware detection often assumes that malicious URLs will be hardcoded or fetched from known domains. But by offloading these URLs to the Ethereum blockchain, hackers bypass both static and dynamic analysis.
Valentić warned:
“It highlights the fast evolution of detection evasion strategies by malicious actors who are trolling open source repositories and developers.”
Ethereum smart contract malware refers to malicious code or instructions hidden within smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain, often used to evade detection by traditional cybersecurity tools.
The attackers embedded URLs inside smart contracts. The infected NPM packages queried the blockchain to fetch these URLs, which were then used to download the actual malware.
Because blockchain interactions appear legitimate and are often encrypted, they bypass many traditional malware detection methods, including firewalls and URL filtering.
Use package auditing tools like Snyk or npm audit
Verify the credibility of GitHub repositories before use
Monitor outbound traffic to block unusual blockchain queries
Keep security software up to date
No. Similar tactics have been observed on other blockchains like Solana and Bitcoin, indicating a broader trend across the crypto ecosystem.
Subscribe to stay informed and receive latest updates on the latest happenings in the crypto world!

Content Strategist
Subscribe to stay informed and receive latest updates on the latest happenings in the crypto world!
 Figure Heloc(FIGR_HELOC)$1.031.50%
Figure Heloc(FIGR_HELOC)$1.031.50% USDS(USDS)$1.000.05%
USDS(USDS)$1.000.05% Hyperliquid(HYPE)$26.56-5.58%
Hyperliquid(HYPE)$26.56-5.58% Ethena USDe(USDE)$1.000.05%
Ethena USDe(USDE)$1.000.05% Canton(CC)$0.160356-0.47%
Canton(CC)$0.160356-0.47% USD1(USD1)$1.00-0.03%
USD1(USD1)$1.00-0.03% Rain(RAIN)$0.0098531.82%
Rain(RAIN)$0.0098531.82% World Liberty Financial(WLFI)$0.107178-8.72%
World Liberty Financial(WLFI)$0.107178-8.72% MemeCore(M)$1.400.57%
MemeCore(M)$1.400.57% BlackRock USD Institutional Digital Liquidity Fund(BUIDL)$1.000.00%
BlackRock USD Institutional Digital Liquidity Fund(BUIDL)$1.000.00% Falcon USD(USDF)$1.000.02%
Falcon USD(USDF)$1.000.02% Aster(ASTER)$0.69-2.17%
Aster(ASTER)$0.69-2.17% Global Dollar(USDG)$1.00-0.02%
Global Dollar(USDG)$1.00-0.02% Bittensor(TAO)$165.60-4.29%
Bittensor(TAO)$165.60-4.29% Circle USYC(USYC)$1.120.00%
Circle USYC(USYC)$1.120.00% Ripple USD(RLUSD)$1.00-0.01%
Ripple USD(RLUSD)$1.00-0.01%